Preclinical imaging at location VUmc
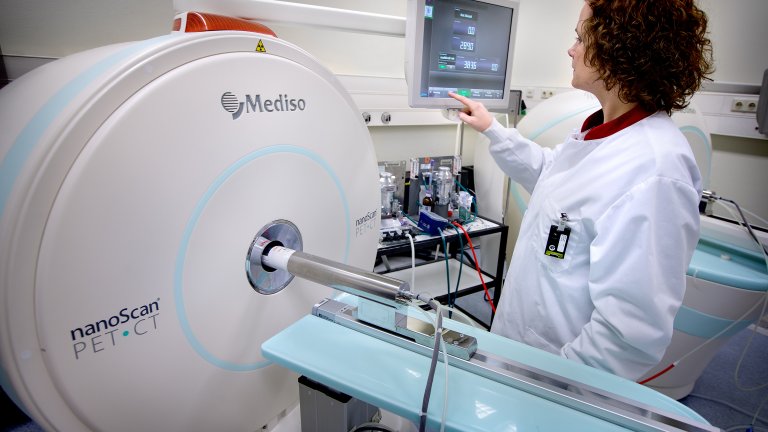
PET imaging
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a molecular imaging techniques that uses radioactive compounds called radiotracers to visualize and measure physiological and biochemical processes in the body. Two state of the art nanoScan PET/CT and PET/MRI (Mediso) are available with a sequential acquisition of PET and anatomical CT or MRI images allowing accurate localization of the radiotracer distribution in the organs. The scanners can accommodate mice and rats. Analysis software and workstation are available for image analysis with extra modules allowing brain segmentation (brain atlas). PET imaging offers unique possibilities for in vivo evaluation and quantification of drugs biodistribution, kinetics, and target engagement. It is also a powerful tool to study disease mechanisms and evaluate therapeutic outcomes.
Optical imaging
Optical imaging offers unique possibilities for in vitro and in vivo imaging applications, especially in the context of molecular imaging. With the Bruker Xtreme imaging system it is possible to acquire bioluminescence, fluorescence and 3D fluorescence images. The system is also equipped with an X-ray source that give access to morphological information and can be overlaid with the fluorescence and bioluminescence images for optimal localization of the signal. This imaging system is highly sensitive and can image fluorescent and/or bioluminescent reporters and probes both in vivo and ex vivo. This imaging module is user friendly and allows rapid and quantitative assessment of fluorescence and bioluminescence in 3-5 mice simultaneously.
Ex vivo and in vitro imaging techniques
Ex vivo validation is an important step in the development process of imaging compounds. The preclinical imaging facility is equipped with state of art Zeiss Axio Observer Z1 fluorescence microscope, and a phosphor imager for autoradiography.
Animal housing facility
The preclinical imaging facility at location VUmc is equipped with a dedicated small animal housing facility with two separate rooms for housing mice and rats. When conducting imaging studies with radiolabeled compounds animals are housed at this facility that is also located inside the radioactive barrier. The facility is equipped with IVC racks allowing the housing of immunocompetent and immunocompromised mice and rats, BSL-2 flow hood for safe working with animals and GMO material, and dumping stations that reduce exposure to animal allergens. Surgery and experimental rooms are available and equipped with stereotactic frame, surgical microscopes and anesthesia devices.
Preclinical imaging at location AMC
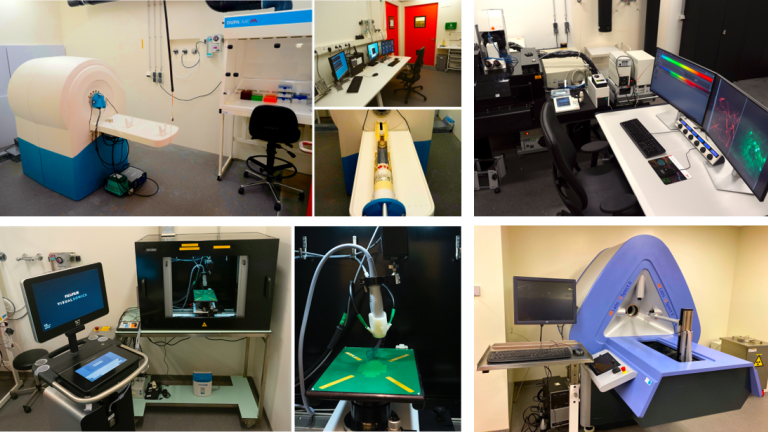
Magnetic resonance imaging
The lab is equipped with a state-of-the-art 7T small animal cryogen free MR system (MR Solutions, Gilford, UK). MRI enables non-invasive, high-resolution anatomical imaging with excellent soft-tissue contrast and unlimited penetration depth. It is therefore suitable to longitudinally study a large range of animal models in the fields of oncology, cardiology, neurology and regenerative medicine. MRI not only sensitively detects various pathological changes in tissue structure, such as edema, fibrosis, calcification, but also enables characterization of a variety of physiological measures, such as diffusion, perfusion, flow and motion (e.g. cardiac function).
Ultrasound and photoacoustic imaging
A VEVO 3100 LAZR-X Photoacoustic Ultrasound system (FujiFilm VisualSonics, Amsterdam, NL) is available for use in mice and rats with automatic 3D motion capabilities. The system has several functionalities installed, such as Color Doppler, Power Doppler, Tissue Doppler, Contrast Imaging and ECG triggered measurements. Dedicated image analysis software is available to process the Ultrasound data. Finally, our LAZR-X system allows novel revolutionary photoacoustic imaging, which combines the rich contrast of optical excitation and deep penetration of ultrasound. This allows for example the quantification of tissue oxygenation by measuring the absorption of both oxy- and deoxyhemoglobin.
3D fluorescence imaging
The department of Biomedical Engineering and Physics hosts two 3D fluorescence imaging cryomicrotome systems (3D-FICS), both uniquely capable of reconstructing volumes of whole organs or small animals with high spatial resolution (8-32 micrometer) while co-localizing the detailed structural information with fluorescent (bio)marker activity across a wide spectral range. By alternately sectioning and imaging, the system acquires 3D, high-resolution, large field of view, anatomical and multispectral molecular fluorescence image volumes from sequential images of the tissue block face. The 3D-FICS allows interrogation of deeper tissues where target-specific interactions can be determined precisely by sections. Such a system offers widespread use in pre-clinical studies involving multimodal molecular imaging co-registered with multispectral probe visualization for disease progression and pathology, early response to therapy, and receptor-targeted applications and probe development.
SPECT imaging
For radionuclide imaging the lab is equipped with the U-SPECT-II (MILabs, Utrecht, NL). The SPECT system uses multi-pinhole cylindrical collimators to meet specific ultra-high resolution and ultra-sensitive imaging requirements. It can perform quantitative 3D functional imaging of SPECT tracers with uniform resolution down to 0.35mm in mice and 0.85mm in rats. Multiple SPECT isotopes can be imaged simultaneously and can be selected in retrospect. SPECT imaging enables real-time in vivo imaging to study e.g. metabolic changes, cerebral blood flow and oxygen levels across models of neurological diseases including Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
Multi-photon imaging
A Leica TCS SP8 multi-photon microscope is available, with a SpectraPhysics Deepsee Insight laser for multiphoton and OPO excitation (680-1300nm, tunable), a fixed 1040nm laser and a 488nm laser. Using the galvano and resonant scanner (up to 8000 Hz), fluorescent labeled compounds targeting specific (cellular) structures can be imaged with both high depth (up to 1mm) as well as high temporal resolution in the living animal. Furthermore, the dual laser set-up allows simultaneous excitation and imaging of multiple fluorescent labels, drastically reducing the scanning time and increasing readout possibilities.
Animal housing facility
All major preclinical imaging equipment at location AMC are combined within the ARIA IWO building, together with the availability of surgical rooms and housing facilities for mice and
rats. This allows easy transfer of animals between the different available imaging modalities and the possibility to perform imaging experiments before and after surgical interventions.
Links
- National collaborative network of experimental & preclinical imaging facilities https://www.amice-imaging.nl/

