To gain insight into the gene expression profile of white and grey matter lesions in MS, Van Wageningen, Van Dam and their colleagues performed RNA sequencing on post-mortem human brain material of MS patients. Leukocortical lesions, comprising white and grey matter areas, and adjacent normal appearing white and grey matter were laser captured and used as input for RNA sequencing.
Data analysis revealed that only 10% of the regulated genes overlapped between white and grey matter lesion areas with oligodendrocyte/myelin related genes being most prominent and reflecting demyelination. In addition, genes related to astrocytic and neuronal/axonal changes were most prominently regulated in white matter lesions. In both lesion areas inflammation-related genes were regulated, but not similar ones. Of interest is the pronounced regulation of microglial ITGAX (CD11c) in grey matter lesions, which may be neuroprotective. Some expression data have been validated by immunohistochemistry.
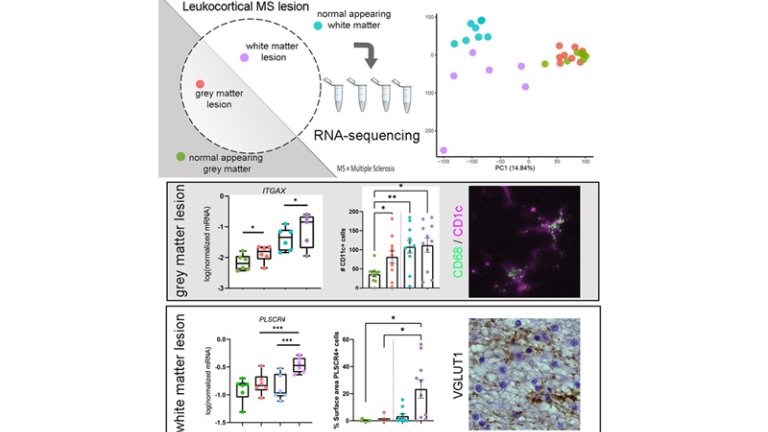
The observed distinct gene expression profile in white versus grey matter MS lesions suggest that different cellular and molecular processes underlie the local demyelination pathology. Current drug treatment of patients with MS is focused on reducing influx and action of inflammatory cells as present in white matter lesions. The researchers propose that targeting additional grey matter specific MS pathology associated genes could possibly be more beneficial for treatment of patients with MS.
Read the publication in Brain Communications: Distinct gene expression in demyelinated white and grey matter areas of patients with multiple sclerosis
Dutch MS Research Foundation supported this research project.